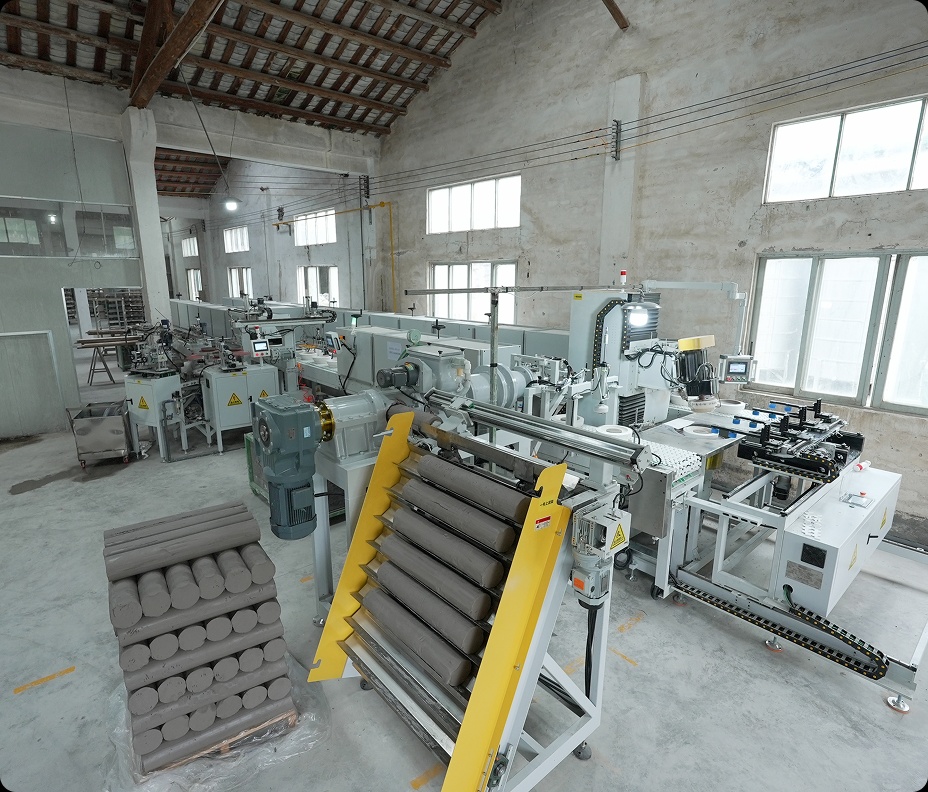
The Shift Toward Automated Ceramic Manufacturing
The global ceramic industry is undergoing a rapid digital transformation.
Traditional production lines rely heavily on manual operations for forming, glazing, and firing, which leads to inconsistent quality and limited scalability.
Factories facing labor shortages, rising energy costs, and tighter quality demands are now turning to automation systems that integrate mechanical, electrical, and software control layers into one coordinated network.
According to the Ceramic Industry Association, plants that adopted full automation achieved up to 45% higher production efficiency and 70% reduction in quality variation compared to manually controlled facilities.
What Is a Ceramic Production Automation System?
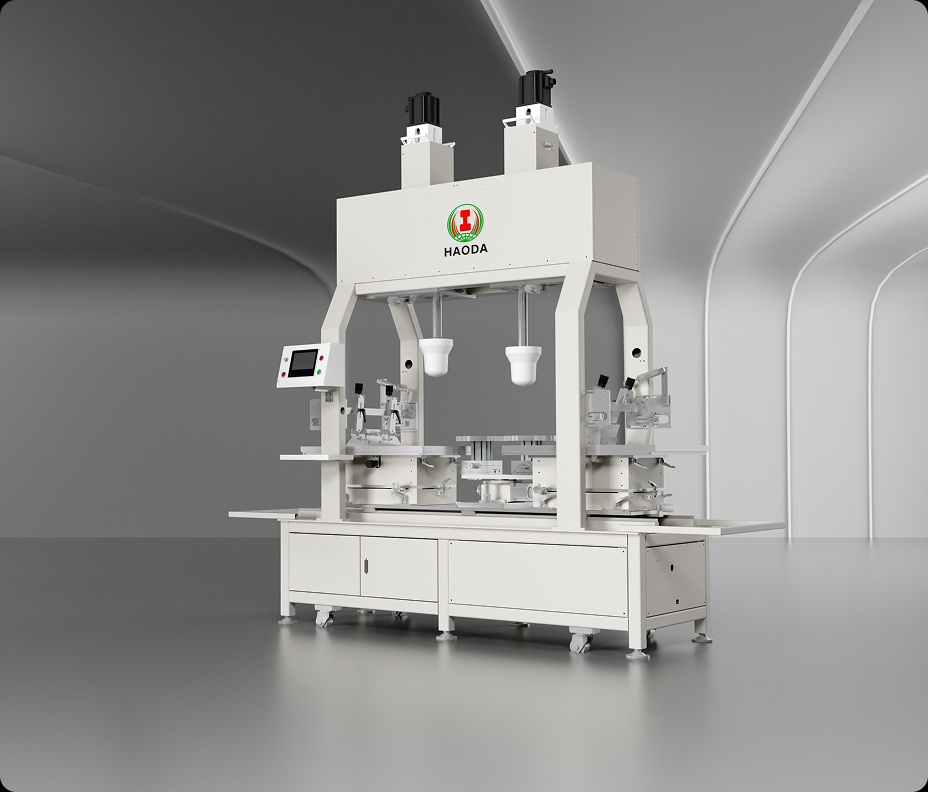
A ceramic production automation system unifies mechanical hardware and digital software into a single smart control framework.
Core Components
| Layer | Function | Example System |
|---|---|---|
| Device Layer | Sensors, actuators, servo motors | Temperature, pressure, and position sensors |
| Control Layer | PLC / CNC controllers | Siemens S7, Mitsubishi, or Delta PLCs |
| Supervisory Layer | SCADA and MES systems | Visual monitoring and production scheduling |
| Management Layer | ERP integration | Order tracking, energy cost analysis |
| AI & Analytics Layer | Predictive maintenance, defect analysis | Machine learning models for performance tuning |
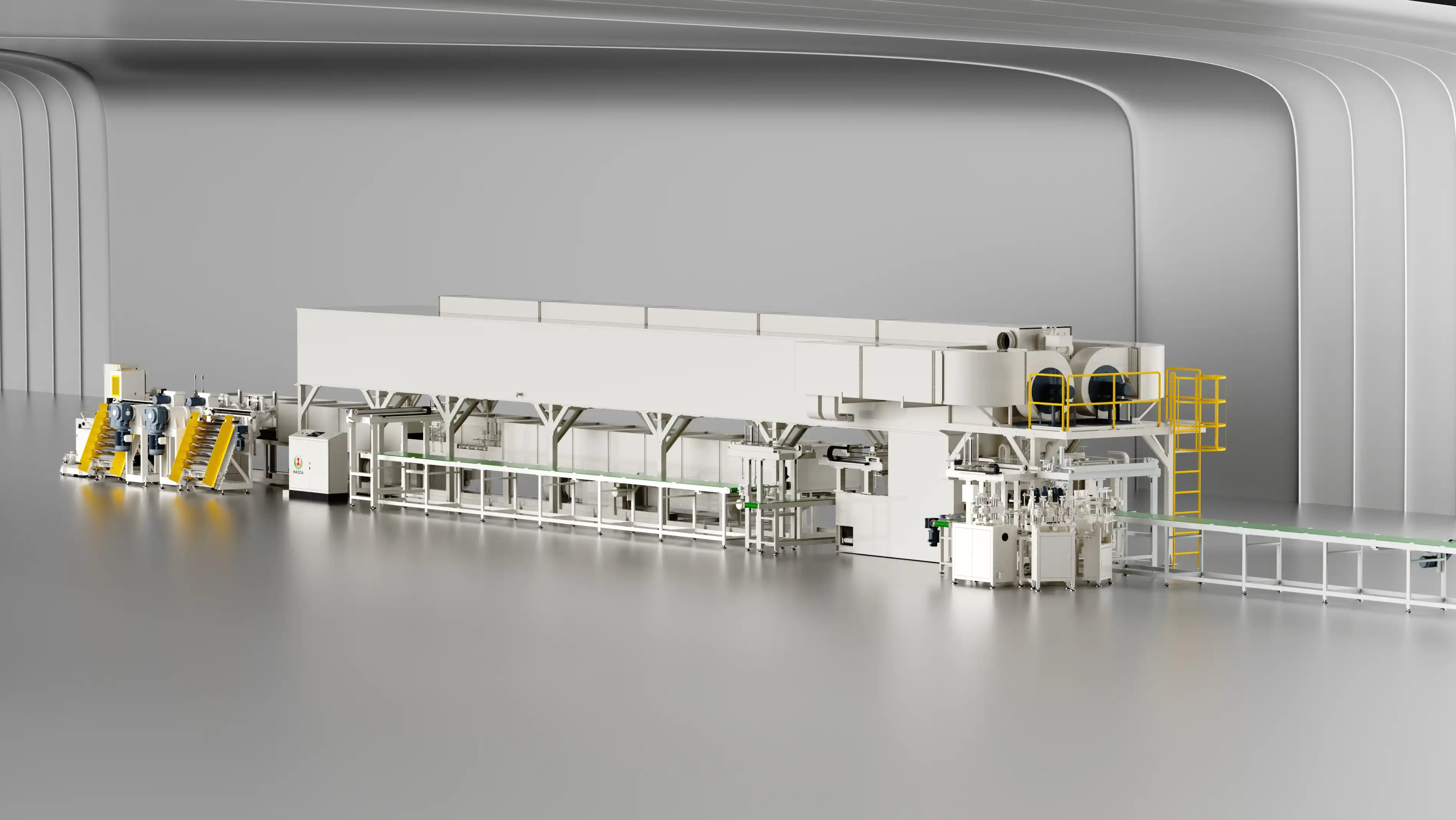
This multi-level architecture ensures real-time synchronization among forming, glazing, firing, and inspection equipment.
Process Synchronization and Control Logic
Automation transforms ceramic production from a linear workflow into a closed-loop feedback system.
-
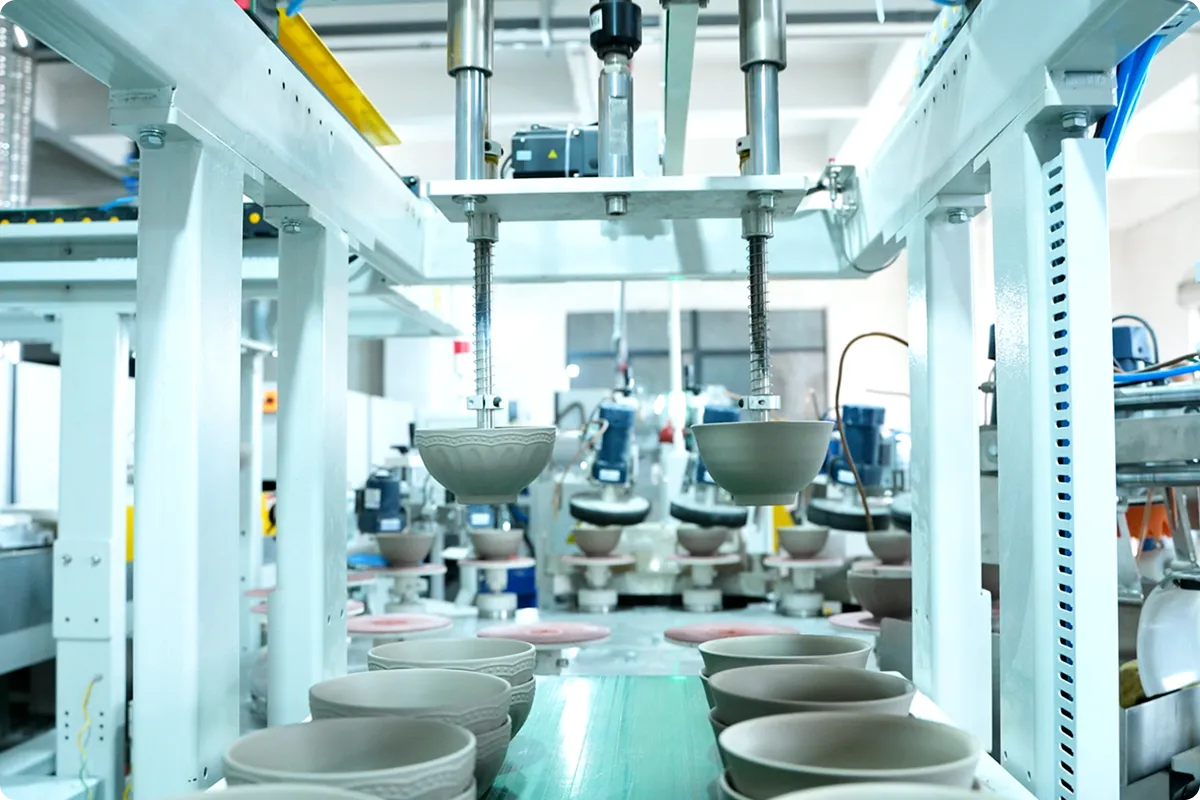
Forming Automation – Servo-driven jiggering and casting machines automatically adjust molding pressure and speed based on clay viscosity.
-
Glazing Automation – Robotic sprayers adapt spray angles and flow rates using computer vision analysis.
-
Firing Control – Kiln temperatures are PID-regulated within ±2°C, ensuring consistent vitrification and color tone.
-
Finishing and Inspection – AI-powered cameras detect glaze defects and surface inconsistencies in real time.
-
Data Transmission – PLCs feed data into SCADA dashboards for centralized visualization and alarm management.
Every station communicates through industrial Ethernet protocols (Profinet / Modbus TCP), enabling full coordination and data traceability.
Quantified Performance Benefits
| Metric | Conventional Line | Automated System | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Output | 1,000 pcs/hr | 2,200 pcs/hr | +120% |
| Energy Efficiency | 100% baseline | 82% baseline | -18% |
| Rejection Rate | 9–10% | 2–3% | -70% |
| Operator Requirement | 10–12 staff | 4–5 staff | -60% |
| Maintenance Downtime | 8 hrs/week | <3 hrs/week | -62% |
Data verified by Manufacturing Automation Journal.
Key Functional Advantages
1. Real-Time Data Acquisition
Sensors continuously collect data on temperature, pressure, glaze thickness, and humidity — forming the foundation for process optimization.
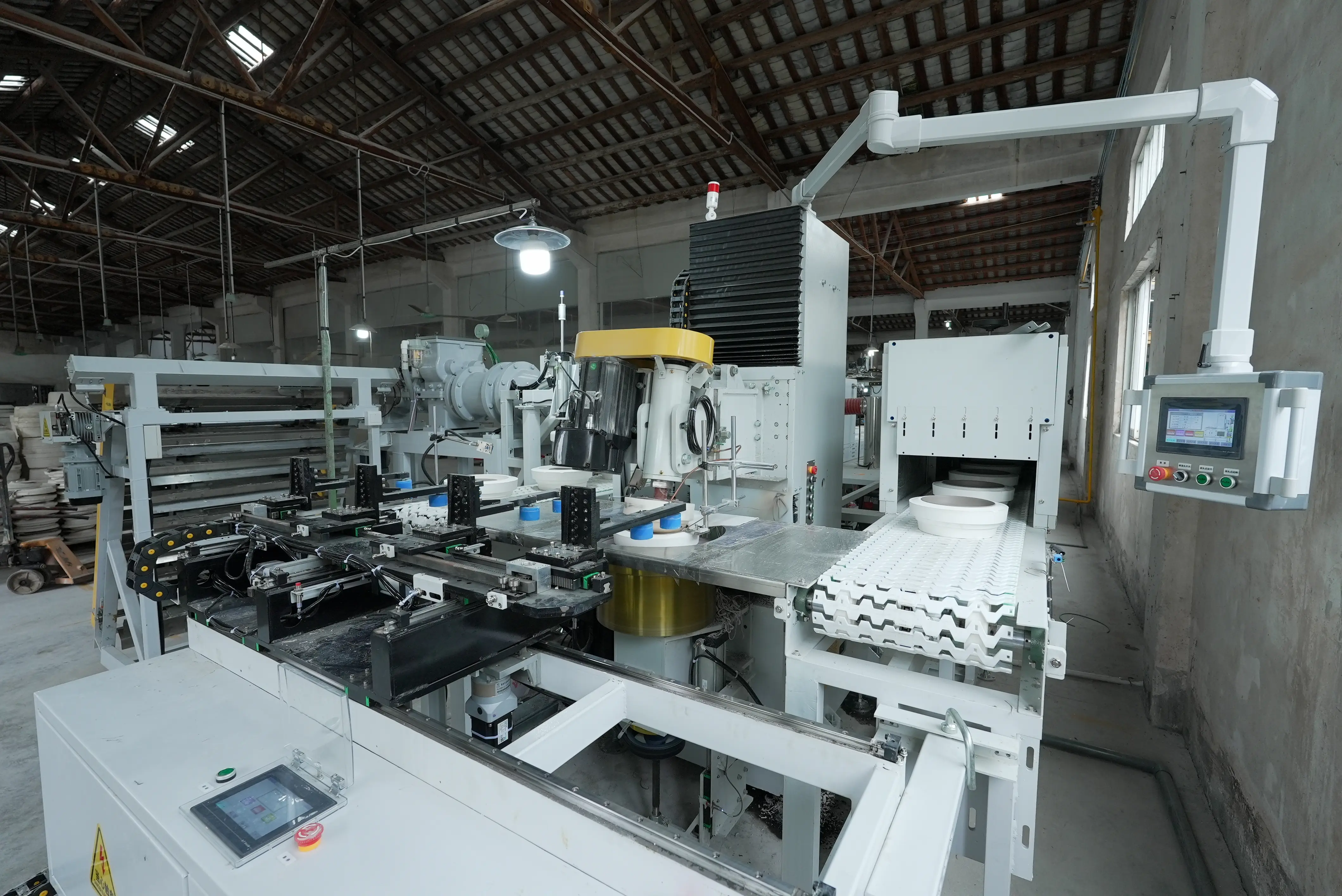
2. Centralized PLC & SCADA Control
Operators can visualize every machine’s status on a unified control screen, modify parameters instantly, and track production cycles in real time.
3. Predictive Maintenance via AI Analytics
Algorithms analyze vibration and motor current data to detect potential faults before they cause downtime.
4. Recipe Management System
Different product designs — plates, mugs, or bowls — can be stored as digital “recipes,” enabling one-click reconfiguration for diverse production runs.
5. MES Integration
Manufacturing Execution Systems link production planning with actual equipment performance, automatically adjusting schedules based on output rate and kiln availability.
ROI and Cost Reduction
| Category | Manual Control | Automated System | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Labor Cost | USD 180,000/year | USD 90,000/year | -50% |
| Energy Consumption | 100% baseline | 82% baseline | -18% |
| Defect Rate | 8–10% | 3% | -65% |
| Maintenance Cost | USD 25,000/year | USD 15,000/year | -40% |
| ROI Payback | — | 16 months | — |
Automation investment is typically recovered within 12–18 months, driven by energy efficiency and reduced waste.
Integration with Digital Manufacturing Systems
The ceramic production automation system can interface with factory-wide digital platforms, including:
-
ERP Systems for order management and inventory tracking
-
IoT Platforms for real-time machine health monitoring
-
Cloud Dashboards for remote supervision
-
Energy Analytics Tools for cost and carbon footprint tracking
Integration with Energy Efficiency Council standards ensures measurable sustainability benefits.
Environmental and Compliance Benefits
Haoda’s systems are built for compliance with ISO 50001 and CE safety directives.
Key features include:
-
Energy reuse in drying and firing stages
-
VOC and dust emission control systems
-
Water recycling and filtration modules
-
Operator safety interlocks and smart emergency protocols
These not only reduce environmental impact but also meet ESG performance expectations for export-oriented ceramic plants.
Implementation and Support
A typical installation process includes:
-
Pre-Project Assessment: Process analysis and line design.
-
System Integration: PLC configuration, device mapping, and signal calibration.
-
Operator Training: SCADA interface, troubleshooting, and maintenance sessions.
-
After-Sales Service: Remote monitoring, software updates, and 24/7 technical assistance.
For automation consultation or line integration support, visit Haoda Machine or contact our technical team.