The Future of Ceramic Manufacturing Lies in Automation
As ceramic production scales globally, the need for precision, speed, and repeatability becomes critical.
Manual operations once defined the ceramic industry—but they now struggle with high labor costs, inconsistent quality, and unpredictable lead times.
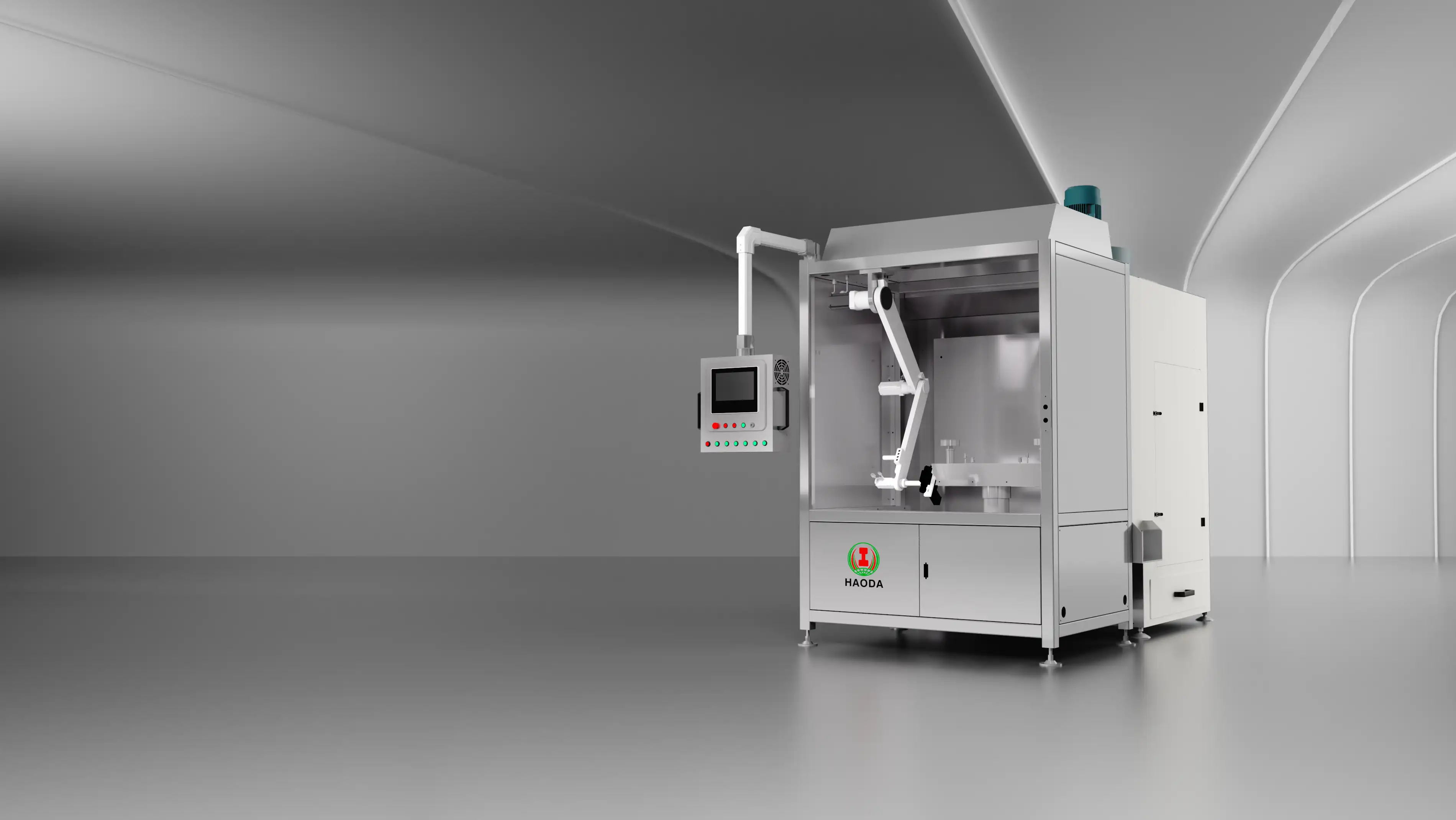
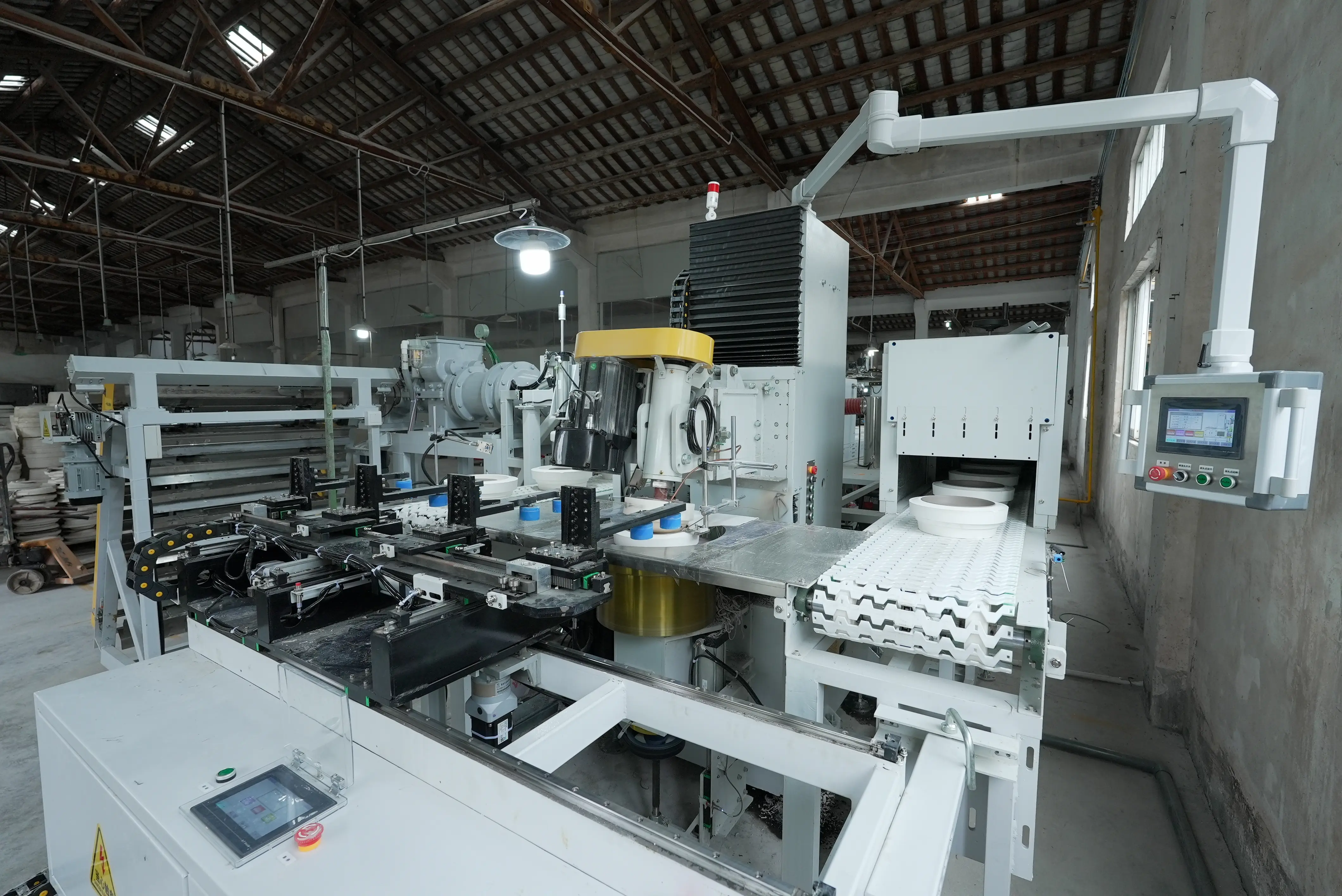
A transition toward ceramic factory automation allows producers to integrate robotics, servo-based forming systems, and MES data control into a unified network.
The International Federation of Robotics estimates that industrial robotics adoption in ceramics manufacturing grew 28% year-over-year, highlighting an accelerating modernization trend.
Components of a Fully Automated Ceramic Factory
| Section | System Type | Automation Role | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forming Station | Roller & pressure casting machines | Servo-controlled shaping | ±0.2 mm precision |
| Glazing Unit | Robotic spray and dip systems | Uniform coating | 25% material saving |
| Printing Module | Pad or digital inkjet | Pattern automation | Design repeatability |
| Drying & Kiln | Energy recovery + AI temperature mapping | Controlled firing | -20% energy loss |
| Quality Inspection | Vision-based defect detection | Inline quality check | 98% accuracy |
| Control Center | PLC + MES integration | Real-time data flow | Full process visibility |
Together, these modules form the backbone of ceramic factory automation, enabling both mass production and customization without compromising efficiency.
Automation Technology Highlights
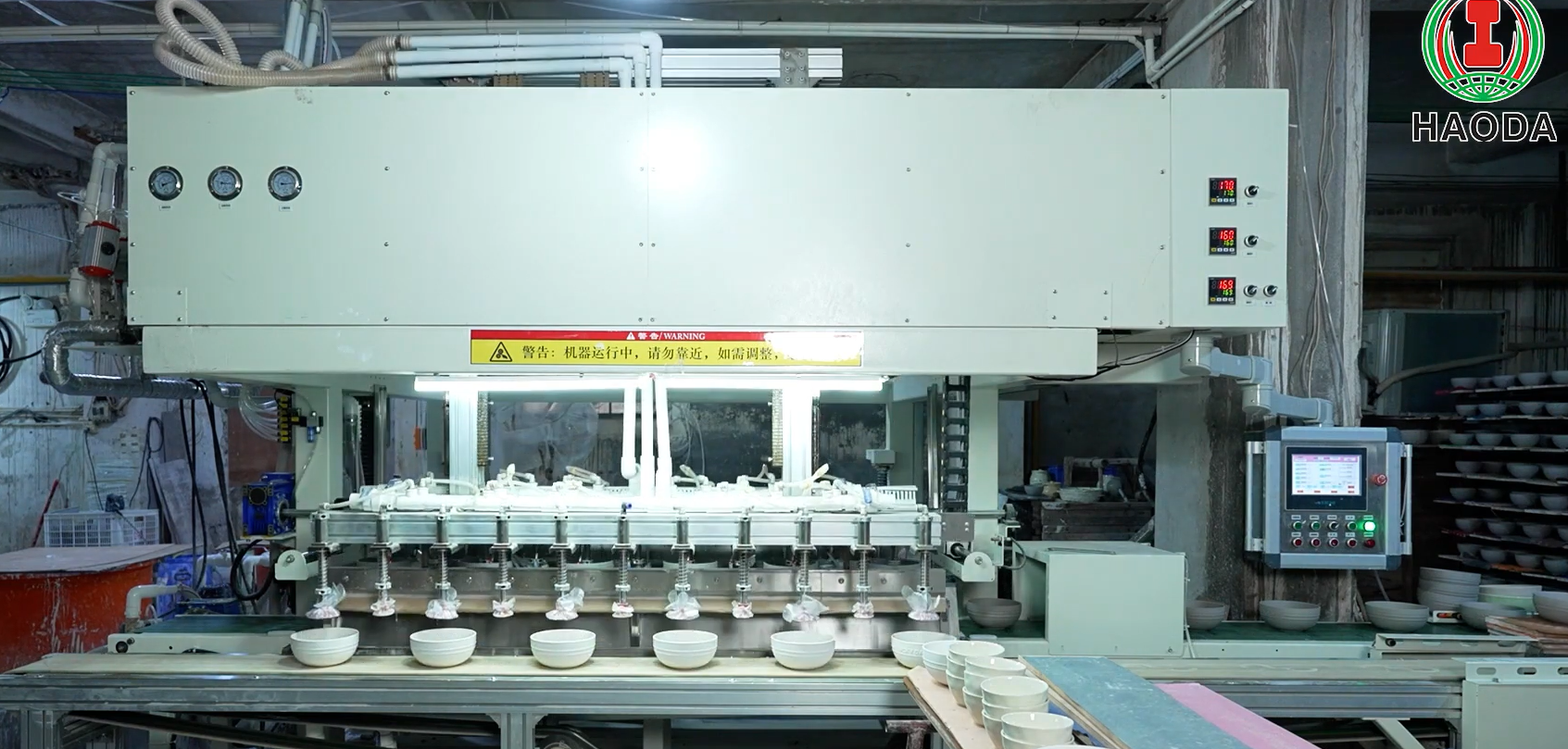
1. Robotic Forming and Handling
Robotic arms equipped with pressure sensors automatically transfer ware between stages, minimizing deformation and human error.
Cycle times drop by 40–50%, while worker safety and line continuity improve substantially.
2. Digital Glazing Optimization
Servo-driven spray systems adjust flow and pressure based on ware geometry.
By reducing overcoating and recycling unused glaze, factories save up to 18% in glaze material costs.
3. AI-Powered Quality Control
Cameras and AI algorithms inspect cracks, pinholes, and deformation in real time, ensuring only defect-free products reach the kiln.
4. Data Synchronization via MES
All machines communicate through an MES (Manufacturing Execution System), which logs production metrics, downtime, and resource use.
This data-centric approach transforms decision-making from reactive to predictive.
Comparative Analysis: Manual vs. Automated Ceramic Production
| Metric | Manual Factory | Automated Factory | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | Baseline | +70% | Faster output |
| Labor Cost | High | -60% | Reduced dependence |
| Quality Consistency | Variable | ±0.2 mm | Stable quality |
| Energy Use | 100% baseline | -25% | Lower consumption |
| Defect Rate | 7–8% | 2–3% | -60% defects |
| ROI Cycle | 3–4 years | 1.5 years | Faster payback |
The result: ceramic factory automation not only cuts operating costs but also secures long-term scalability and resilience.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Sustainability is now an integral part of automation.
Advanced ceramic lines employ:
-
Heat Recovery Systems – capturing and reusing kiln exhaust to preheat incoming ware.
-
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) – adjusting motor power in real time to reduce waste.
-
Air & Water Recirculation Loops – conserving up to 25–30% of resources.
-
Digital Energy Dashboards – tracking kilowatt and gas consumption per product batch.
According to the Clean Manufacturing Alliance, automation-based factories can achieve 20–35% lower carbon intensity compared to non-automated plants.
Global Automation Projects by Haoda Machine
Haoda Machine has implemented full ceramic factory automation solutions for factories in Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
-
Vietnam / China: Dual forming lines and robotic glazing integration for large-scale porcelain tableware.
-
Turkey / Poland: MES-based production with adaptive scheduling for mixed product batches.
-
Saudi Arabia / UAE: AI-inspection and smart kiln coordination for high-end hotelware lines.
-
Egypt / Brazil: Mid-size production systems focused on energy savings and digital traceability.
Each case demonstrates how flexible automation adapts to production scale and regional infrastructure.
ROI Perspective: The Business Case for Automation
| Cost Aspect | Before Automation | After Automation | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Labor Expenses | 100% baseline | 40% | -60% |
| Material Loss | 8% | 3% | -62% |
| Production Downtime | 6 hours/month | <2 hours | -65% |
| Maintenance Frequency | High | Scheduled predictive | -45% |
| Overall ROI | 36 months | 16–18 months | 2× faster recovery |
For investors, automation shortens payback periods while improving consistency, traceability, and brand credibility.
Intelligent Manufacturing with Haoda Machine
Haoda Machine provides turnkey automation solutions—from mechanical forming to data systems integration—ensuring each production line runs at maximum efficiency.
Core Advantages Include:
-
Integrated forming, glazing, and quality systems
-
PLC + MES network for digital production control
-
Predictive maintenance for reduced downtime
-
Global technical support and operator training
-
Customizable modular design for different capacities
By adopting ceramic factory automation, manufacturers can achieve superior productivity, lower costs, and a sustainable manufacturing footprint.
To explore Haoda’s automation frameworks and reference projects, visit Haoda Machine’s homepage for detailed solutions.
For personalized consulting or to plan your factory automation roadmap, contact our automation specialists—we’ll help you define your technical path, investment scale, and ROI timeline.